What began as a response to workforce shortages and rising imaging volumes has evolved into a broader ecosystem of hardware, cloud platforms, and value-added services. This FAQ explains what this means for providers, manufacturers, and service partners.
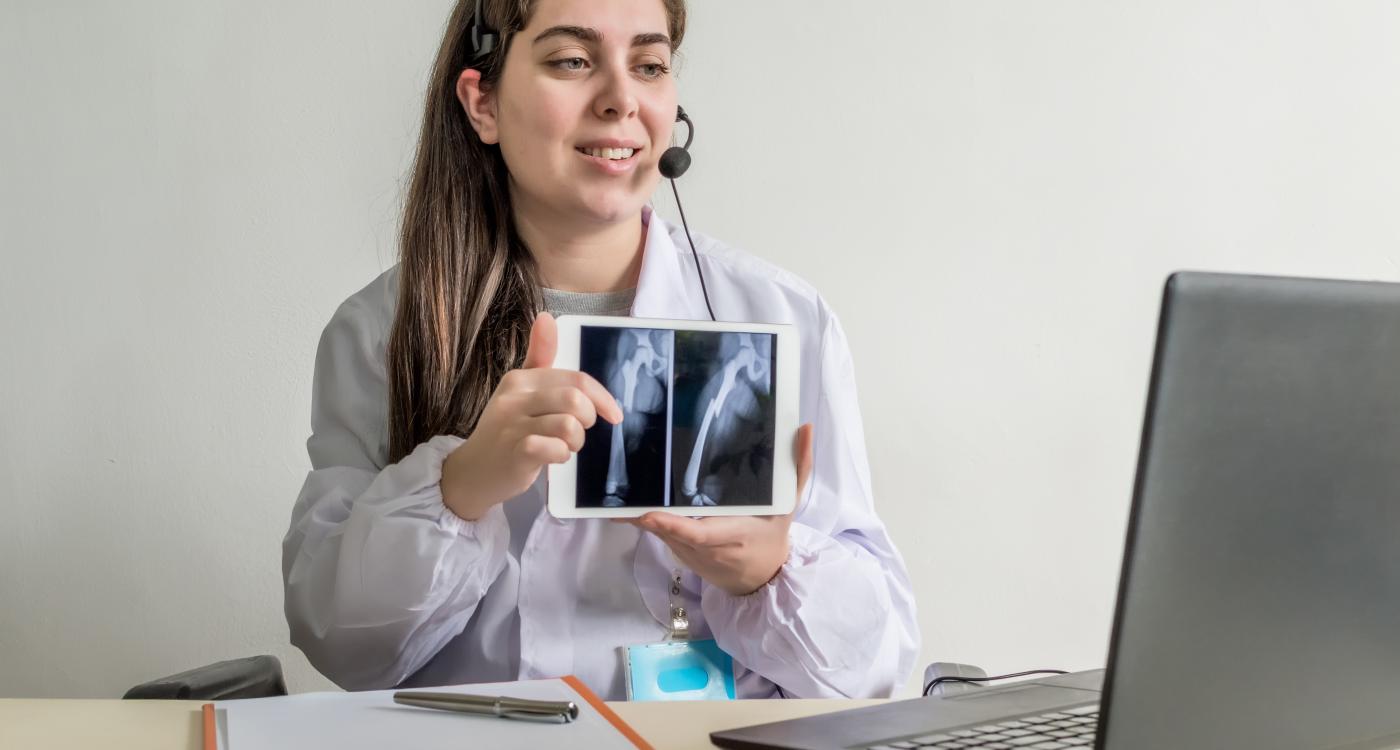
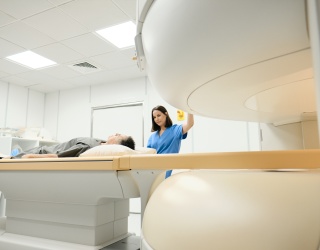
Remote radiology, or teleradiology, is the practice of interpreting medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans from outside the healthcare facility where they are generated. By supporting remote workstations, it increases efficiency, reduces patient wait times, enables faster treatment decisions, improves collaboration among healthcare professionals, and expands specialized services to rural and underserved regions.
Why is demand for remote workstations and services increasing?
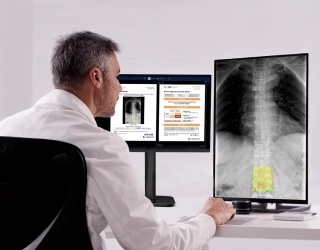
Radiology is under pressure from multiple directions: shortages of qualified staff, growing imaging demand linked to aging populations and chronic diseases, and limited access to specialized radiologists. Remote workstations supported by cloud PACS systems help close these gaps by enabling image access and flexible reporting models that enable faster diagnoses.
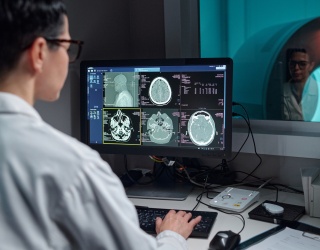
Teleradiology reduces turnaround times, improves collaboration, and supports talent retention by allowing radiologists to work remotely. The integration of AI and machine learning into PACS further accelerates reporting and improves diagnostic accuracy and workflow efficiency. Cloud-based systems also reduce capital expenditure on hardware and IT infrastructure, making them attractive for hospitals and imaging centers.
What new business models are emerging?
The shift toward remote infrastructure is reshaping business approaches. The most significant change is the move from one-time hardware sales to ongoing service contracts. Providers now expect bundled solutions that integrate displays, PACS access, calibration software, and cybersecurity compliance.
This opens doors for manufacturers to offer predictive maintenance services, subscription-based quality control, and remote fleet management dashboards. For service providers, opportunities lie in offering 24/7 remote monitoring, compliance auditing, and workflow integration support. High-specification medical displays remain standard at fixed workstations, but portable systems are gaining ground in outpatient and bedside care. For example, mobile imaging solutions, such as handheld ultrasound and low-field MRI systems, are extending diagnostics to rural and emergency settings, reducing costs by 80% while maintaining diagnostic quality.
Which regulatory requirements play a role?
Data protection and cybersecurity are central. HIPAA in the US and GDPR in Europe mandate strict encryption and access protocols. The FDA and EU authorities are also setting expectations for secure boot functions, encrypted data exchange, and vulnerability management in connected devices. Likewise, regulators are paying closer attention to AI, addressing concerns about transparency and bias in algorithm-based decision support tools.
Sustainability is also gaining importance. Programs like the FDA’s Green Imaging Initiative set energy-efficiency targets, while manufacturers are prioritizing eco-friendliness to reduce energy consumption and carbon footprints.
Compliance is now a competitive differentiator. Vendors able to guarantee data security, audit trails, and DICOM-conformant display performance gain an advantage.

What technologies are needed for remote QC and monitoring?
Remote monitoring depends on a combination of advanced hardware and software:
- Cloud-based PACS systems for secure image access and collaboration
- Calibration and QC software to ensure consistency across sites
- Centralized dashboards for monitoring and reporting
- Hybrid cloud deployments balancing reliability with scalability for optimal functionality and security
- AI-powered imaging tools for automated image analysis and workflow optimization
- Interoperability solutions to integrate systems for seamless data exchange
- Security features to meet healthcare IT standards
Where is the market headed?
Remote workstations will continue to evolve from isolated hardware toward fully integrated ecosystems that combine displays, PACS access, monitoring, compliance, and service layers. Growth will be strongest in underserved regions, ambulatory surgical centers, and places where remote access is critical.
For providers, this means rethinking business models: recurring service contracts, predictive monitoring, and AI-powered support will be as important as hardware specifications. For manufacturers, aligning R&D with regulatory and sustainability requirements while expanding into software and cloud services is key.
The opportunity is significant: The global medical display market is projected to grow from USD 2.58 billion in 2025 to USD 3.26 billion by 2030 (Mordor Intelligence). Remote infrastructures will not only address workforce shortages but also create long-term, service-driven business models.